Epirus water frog Description Distribution and habitat References Navigation menu"Pelophylax epeiroticus"10.2305/IUCN.UK.2009.RLTS.T58592A11793456.en5027pelophylax-epeiroticus3326562426648663217751855859270701expanding ite
IUCN Red List vulnerable speciesPelophylaxAmphibians of EuropeAmphibians described in 1984True frog stubs
frogRanidaeKerkyrahuman consumptionhabitat lossvulnerable
| Epirus water frog | |
|---|---|
 | |
Conservation status | |
 Vulnerable (IUCN 3.1)[1] | |
Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Ranidae |
| Genus: | Pelophylax |
| Species: | P. epeiroticus |
Binomial name | |
Pelophylax epeiroticus (Schneider, Sofianidou & Kyriakopoulou-Sklavounou, 1984) | |
 | |
Synonyms | |
Rana epeirotica Schneider, Sofianidou & Kyriakopoulou-Sklavounou, 1984 | |
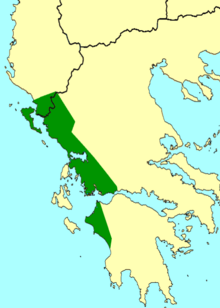
The Epirus water frog (Pelophylax epeiroticus) is a species of frog in the family Ranidae. It is found in western Greece, including Kerkyra, and the southern areas of Albania. The species is collected from the wild for human consumption.
Description
Like most frogs, Epirus water frogs show sexual dimorphism. Males can grow to 2.9 inches (74 mm) in length, with females growing larger to 3.3 inches (84 mm). The dorsal side is typically green with irregular black spots. The underside is pale. Male vocal sacs are olive aside from mating season, when they can turn a dark gray.
Distribution and habitat
The species occurs in Mediterranean-type shrubby vegetation, rivers, swamps, freshwater lakes and marshes, and plantations. It is threatened by habitat loss, and is classified as vulnerable as populations within its relatively small range are fragmented.[1]
References
^ ab Uzzell, T.; Lymberakis, P.; Haxhiu, I. (2009). "Pelophylax epeiroticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2009: e.T58592A11793456. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2009.RLTS.T58592A11793456.en. Retrieved 5 July 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
This true frog article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Amphibians described in 1984, Amphibians of Europe, IUCN Red List vulnerable species, Pelophylax, True frog stubsUncategorized