Werder (Havel) Contents Etymology History Demography Politics Economics Notable people Gallery International relations See also References External links Navigation menu52°22′41″N 12°56′06″E / 52.37806°N 12.93500°E / 52.37806; 12.9350052°22′41″N 12°56′06″E / 52.37806°N 12.93500°E / 52.37806; 12.93500www.werder-havel.de"Bevölkerungsentwicklung und Flächen der kreisfreien Städte Landkreise und Gemeinden im Land Brandenburg - 2017""Alle politisch selbständigen Gemeinden mit ausgewählten Merkmalen am 31.12.2018 (4. Quartal)"the original"Bevölkerung im Land Brandenburg nach amtsfreien Gemeinden, Ämtern und Gemeinden 31. Dezember 2017 (Fortgeschriebene amtliche Einwohnerzahlen auf Grundlage des Zensus 2011)"Population Projection Brandenburg at Wikimedia CommonsWerderWerder (Havel) BlogWerder/HavelCity Council of Werder upon Havel's official websiteOfficial website of Werder (Havel)e4065553-28375d96d-8207-4f31-93e5-aae88681238f
Bad BelzigBeelitzBeetzseeBeetzseeheideBensdorfBorkheideBorkwaldeBrückBuckautalGolzowGörzkeGräbenGroß KreutzHavelseeKleinmachnowKloster LehninLintheMichendorfMühlenfließNiemegkNuthetalPäwesinPlanebruchPlanetalRabensteinRosenauRoskowSchwielowseeSeddiner SeeStahnsdorfTeltowTreuenbrietzenWenzlowWerderWiesenburgWollinWusterwitzZiesar
Towns in BrandenburgLocalities in Potsdam-MittelmarkProvince of BrandenburgBezirk Potsdam
BrandenburgGermanyHavelPotsdam-MittelmarkPotsdamclimateElbeUpper GermanBerlinSlavicBrandenburg margravesLehnin AbbeySwedishThirty Years' WarWorld War IIairplane pilotLuftwaffeKarl KollerBattle of BerlinSovietRussianreunification of GermanyNazi GermanyEast GermanyCensus in GermanyBrandenburgBertelsmann FoundationmayorChristian Democratic UnionSocial Democratic PartyCistercianmonastery of LehnincherriesapplesstrawberriesraspberriesgooseberriescurrantsblackberriesapricotspeachespearsplumsgreenhouseswineMargraviate of BrandenburgHohenzollernFranconiaBrandenburgMoselleviticultureWeißer ElblingWeißerRoter SchönedelRotfrankeWerderaner WachtelbergDornfelderRegentSaphiraMüller-ThurgauPotsdamtwinned![]() Werder (Havel)
Werder (Havel)
Werder (Havel) | |
|---|---|
 City island in the River Havel, with Großer Plessower See in the background | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Werder (Havel) within Potsdam-Mittelmark district  | |
 Werder (Havel) Show map of Germany  Werder (Havel) Show map of Brandenburg | |
| Coordinates: 52°22′41″N 12°56′06″E / 52.37806°N 12.93500°E / 52.37806; 12.93500Coordinates: 52°22′41″N 12°56′06″E / 52.37806°N 12.93500°E / 52.37806; 12.93500 | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Brandenburg |
| District | Potsdam-Mittelmark |
| Subdivisions | 8 Ortsteile |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Manuela Saß (CDU) |
| Area [1][2] | |
| • Total | 117.05 km2 (45.19 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 31 m (102 ft) |
| Population (2017-12-31)[3] | |
| • Total | 25,695 |
| • Density | 220/km2 (570/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 14542 |
| Dialling codes | 03327 |
| Vehicle registration | PM |
| Website | www.werder-havel.de |
Werder (Havel) (official name derived from Werder an der Havel ("Werder upon Havel"), colloquially just Werder), is a town in the state of Brandenburg, Germany, located on the Havel river in the Potsdam-Mittelmark district, west of the state's capital Potsdam.
Werder has a long and rich history and is a nationally recognized Erholungsort – a government designation given to regions of Germany that have been recognized and must be continuously re-certified as having air and climate qualities which provide a healthful environment to visitors. Werder is also famous for hosting one of Germany's three largest festivals, the Baumblütenfest, held annually in May.
Contents
1 Etymology
2 History
3 Demography
4 Politics
5 Economics
5.1 Viticulture
6 Notable people
7 Gallery
8 International relations
8.1 Twin towns — Sister cities
9 See also
10 References
11 External links
Etymology
The Werder municipal area stretches along the banks of the Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, and the town's oldest quarter is located on an island in the river. Hence the name, as the landscape term Werder (like Wörth in Upper German) means "river island".
History
Werder has several different specific mentions in the ancient historical records of Berlin, which lies 165 km (103 mi) southeast. The city "Werdere" is mentioned in 1317, "Wehrder" in 1450 and in its present spelling in 1580. However, in its southwest end pieces of ancient broken glass have been discovered, and on its south end are remains of what may have been an Early Medieval Slavic castle wall.
The coin-shaped city island in the Havel river is mentioned as being accessible via a bridge in a 1317 deed, when the ministeriales of the Brandenburg margraves had to sell the estates to the monks of nearby Lehnin Abbey. The town was devastated by Swedish troops during the Thirty Years' War.
During World War II and prior thereto an airfield existed in the north of the city which, together with an adjacent park, was used during the war as an airplane pilot training area. Werder was the base of Luftwaffe general Karl Koller during the Battle of Berlin. After the end of the war, Soviet troops were stationed in this area of the city. The last Russian troops departed in 1993, three years after the reunification of Germany.
Demography
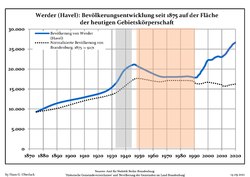
Development of population since 1875 within the current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population development in Brandenburg state; Grey Background: Time of Nazi Germany; Red Background: Time of communist East Germany)
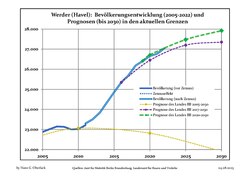
Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany in 2011 (blue bordered line); Projection by the Brandenburg state for 2005-2030 (yellow line); Projection by the Brandenburg state for 2014-2030 (red line); Projection by the Bertelsmann Foundation for 2012-2030 (green line)
| Werder (Havel): Population development within the current boundaries (2017)[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Politics
Since 1990, Werder's mayor has been Werner Große of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), who had previously functioned as the city's deputy. The 29-seat town council (SVV), meets every two months, to represent the interests of the citizenry. The council is composed of 17 CDU members, 4 Social Democratic Party members, 3 Action Free Citizens members and various other unaffiliated city delegates.
There are a number of committees with appointed citizens delegates who consult with the town council. The central committee, which exists under chairmanship of the mayor, deals with finances in consultation with an auditing board of examiners. The committee for social policy, education, culture and sport, oversees area schools. There is also a special committee responsible for town development, construction and living conditions, which has significant influence over the city's infrastructure.
Economics
Although at one time known for its wine production and fishing industry, both pursuits declined during the 18th century. From early times the monks of the Cistercian monastery of Lehnin cultivated fruit in the region and Werder is still today particularly well known for this endeavor, which is also the foundation for its famous blossoming season festival. The predominant fruits grown in the area are cherries, apples, and strawberries but raspberries, gooseberries, currants, blackberries, apricots, peaches, pears, and plums are also cultivated. Vegetables are also grown, especially tomatoes, the bulk of which are cultivated in local greenhouses.
Viticulture
Location of the wineyard in the town
Cultivation of wine is the city's second-oldest trade after fishing, brought to this area before 1300 by monks of the Cistercian Order. The wine of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (Mark Brandenburg) counted at the end of the 13th century to the most important export articles to East and Northern Europe. The Hohenzollern dynasty, they came from Franconia to Brandenburg, made the wine of the Brandenburg March able of court. Up to the death of the Great Elector the wine was drunk in his board. The first Wine Master Order of Brandenburg was already remitted 1598 by the Elector Johann Georg and at that time it was reported which would be surrounded Havel by vineyards like the Moselle. However, the viticulture in this area was not trouble-free. The winters were so hard every now and then on which many vines got frostbite. Thus happen in winter, 1739/40, after the frost stopped till June. In the first half of the 18th century, grapes were grown on more than 100 hectares in Werder. The vines at that time were Weißer Elbling, Weißer and Roter Schönedel and Rotfranke. Nevertheless, more and more red wine than white wine was grown. The Quail's mountain of Werder (Werderaner Wachtelberg) counts to the oldest winegrowing places beyond the island Werder. On the island wine at the Mill Mountain and at the God's Mountain was grown. The wine foliage was used earlier to the envelopment by fruit, especially from apricots and peaches. The fruits could be transported so carefully in the Obsttienen (small transport container made from wood). In 1887 it was still reported about 2 vineyards. The wine cultivation period ended provisionally when the last vines in Werder got frostbite in the winter of 1955/56. Only in 1985 began the Cooperative Society Fruit Production of Werder on the Quail's Mountain with putting on a vineyard on a surface of 4.8 hectares. Today about 30 thousand vines grow there on nearly 7 hectares. If Dornfelder, Regent, Saphira and Müller-Thurgau belong to it among other things. Within the scope of the Federal Garden Show (Bundesgartenschau) in Potsdam Wine Teaching Paths on the Quail's Mountain were put on. Today here grow 38 red and 40 white wine kinds. The vineyard Quail's Mountain of Werder lies geographically with Latitude of 52 degree and 22 minutes north far to the north of the usual winegrowing areas of Europe. In 1991 this vineyard was taken up as a Großlagenfreie Einzellage in the Weinanbaugebiet Saale-Unstrut (winegrowing area at the rivers Saale and Unstrut) and was recognised by the EU. It is with it the most northern registered position for quality-tested wine cultivation (QbA) in Europe and the World.
Notable people
Anna Simson (1835–1916), women's rights activist
Karl Hagemeister (1848–1933), landscape painter
Burglinde Pollak (* 1951), pentathlete
Brigitte Ahrenholz (1952–2018), rower
Adolf Damaschke (1865–1935), politician and economist, lived in Werder since 1907
Bruno Kramm (* 1967), musician
Gallery

The Holy Spirit Church and "Goat's windmill" on the shore of the Havel
Street in bloom on Werder's river island at the end of April, during the blossom festival

Old town hall

Church in Petzow

Petzow Castle

Former wash house in Petzow

Former fire engine house in Petzow

Fisherman's house in Petzow

Church in Plötzin

Former brickyard Löcknitz
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Werder is twinned with:
 Oppenheim, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany
Oppenheim, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany Almdorf, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany
Almdorf, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany Hjørring, Denmark
Hjørring, Denmark Tczew, Poland
Tczew, Poland Biržai, Lithuania
Biržai, Lithuania Muan-gun, South Korea
Muan-gun, South Korea
See also
- Großer Plessower See
References
^ "Bevölkerungsentwicklung und Flächen der kreisfreien Städte Landkreise und Gemeinden im Land Brandenburg - 2017". Statistical office Berlin-Brandenburg. Retrieved 10 March 2019..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Alle politisch selbständigen Gemeinden mit ausgewählten Merkmalen am 31.12.2018 (4. Quartal)". DESTATIS. Archived from the original on 10 March 2019. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
^ "Bevölkerung im Land Brandenburg nach amtsfreien Gemeinden, Ämtern und Gemeinden 31. Dezember 2017 (Fortgeschriebene amtliche Einwohnerzahlen auf Grundlage des Zensus 2011)". Amt für Statistik Berlin-Brandenburg (in German). 2018.
^ Detailed data sources are to be found in the Wikimedia Commons.Population Projection Brandenburg at Wikimedia Commons
Werder, in: Meyers Konversationslexikon, 4. Aufl. 1888-89, Bd. 16, S. 534.- Werder News at the Werder (Havel) Blog.
- Thomas's Glassware Tour 2006. Werder/Havel. Retrieved April 3, 2006.
- Werder upon Havel City Council 2006.City Council of Werder upon Havel's official website. Retrieved April 3, 2006.
External links
![]() Media related to Werder (Havel) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Werder (Havel) at Wikimedia Commons
Official website of Werder (Havel) (in German) + (in English)
Bezirk Potsdam, Localities in Potsdam-Mittelmark, Province of Brandenburg, Towns in BrandenburgUncategorized











