Eratosthenes Seamount See also References External links Navigation menu33°40′N 32°40′E / 33.667°N 32.667°E / 33.667; 32.66733°40′N 32°40′E / 33.667°N 32.667°E / 33.667; 32.667Eratosthenes Seamount: an oceanographic yardstick recording the Late Mesozoic-Tertiary geological history of the Eastern MediterraneanEratosthenes Seamount: the possible spearhead of incipient continental collision in the Eastern MediterraneanEarthref entryexpanding ite
Seamounts of the MediterraneanPhysical oceanographyContinental fragmentsMarine geography stubs
seamountMediterraneanCyprusmassifEratosthenes Abyssal PlainOcean Exploration TrustEV NautilusOttoman4th century BCtrawlers
| Eratosthenes Seamount | |
|---|---|
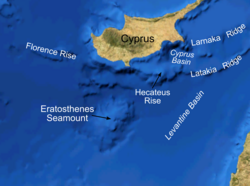 Bathymetric features south of Cyprus | |
| Summit depth | 690 m (2,264 ft) |
| Height | 2,000 m (6,562 ft) |
| Summit area | 120 km × 80 km (75 mi × 50 mi) |
| Location | |
| Location | Eastern Mediterranean |
| Group | Eratosthenes Abyssal Plain |
| Country | 33°40′N 32°40′E / 33.667°N 32.667°E / 33.667; 32.667Coordinates: 33°40′N 32°40′E / 33.667°N 32.667°E / 33.667; 32.667 |
| Geology | |
| Type | Seamount (continental fragment) |
The Eratosthenes Seamount or Eratosthenes Tablemount is a seamount in the Eastern Mediterranean about 100 km south of western Cyprus. It is a large, submerged massif, about 120 km long and 80 km wide. Its peak lies at the depth of 690 m and it rises 2000 m above the surrounding seafloor, which is located at the depth of up to 2,700 m and is a part of the Eratosthenes Abyssal Plain. It is one of the largest features on the Eastern Mediterranean seafloor.
In 2010 and 2012 the Ocean Exploration Trust's vessel EV Nautilus explored the seamount looking for shipwrecks. Three were found; two were Ottoman vessels from the 19th century and the third was from the 4th century BC. Such seamounts are considered to be ideal for the preservation of shipwrecks because at depths of around 600 metres the areas are not disturbed by trawlers or by sediments coming off land.[1]
See also
- CenSeam
- Ferdinandea
References
^ Learn, Joseph Rapp (9 December 2017). "Wayfarers of the ancient world". New Scientist. Vol. 236 no. 3155. p. 12..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
External links
- Mart, Yossi and Robertson, Alastair H. F. (1998). Eratosthenes Seamount: an oceanographic yardstick recording the Late Mesozoic-Tertiary geological history of the Eastern Mediterranean, in Robertson, A.H.F., Emeis, K.-C., Richter, C., and Camerlenghi, A. (eds.), Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 160, Chapter 52, 701–708.
- Kempler, Ditza (1998). Eratosthenes Seamount: the possible spearhead of incipient continental collision in the Eastern Mediterranean, in Robertson, A.H.F., Emeis, K.-C., Richter, C., and Camerlenghi, A. (eds.), Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 160, Chapter 53, 709–721.
- Earthref entry
This article about a specific oceanic location or ocean current is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Continental fragments, Marine geography stubs, Physical oceanography, Seamounts of the MediterraneanUncategorized